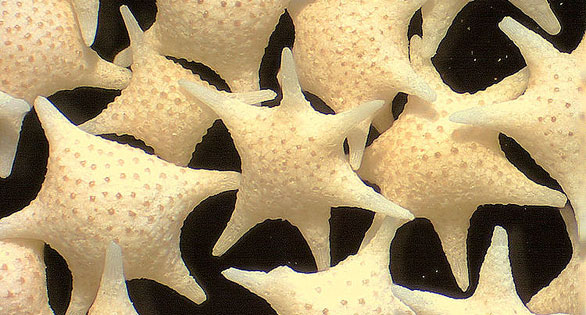
Foraminifera “Star Sand,” Baculogypsina sphaerulata, greatly enlarged. Hatoma Island – Japan. Image: Psammophile.
Most are smaller than a pinhead and are largely unseen by humans who don’t have a magnifying lens in hand, but foraminiferans or “forams” are found in countless numbers on the world’s reefs, often forming part of the matrix of sandy substrate that can fuse into hard areas of calcium carbonate.
Amoeba-like organisms that typically secrete a calcium test or shell to protect their soft bodies, forams are estimated to generate some 43 million tons of reef carbonates each year. Their appearance varies tremendously over an estimated 275,000 species, most all marine bottomdwellers that measure less than 1 mm in diameter. Some species grow larger, including the Red Tree Foram, Holotrema rubrum, which can hitchhike into reef aquaria on live rock (Shimek, 2004).
Now marine scientists are fearful that the entire class of foraminiferans may be among the first group of organisms to disappear as ocean waters become more acidic. In fact, forams as a class may be extinct by the year 2100 say a team of scientists from the Australian Institute of Marine Science (AIMS).
“Forams–or foraminifera –are much like an amoeba with a shell,” explains Dr. Sven Uthicke, lead author of a study which was published in May in the journal Scientific Reports, an online journal of Nature. “As CO2 levels increase, our oceans will become more acidic, making it more difficult for these small marine creatures to form the shells they need to survive.
“These simple organisms are vulnerable to increasing ocean acidification as they lack the complexity and energy reserves of other skeleton-based marine creatures, like corals and sea urchins,” says Uthicke.
Volcanic Vents in New Guinea Provide Clues
“We conducted a study in Papua New Guinea, where subsurface volcanic activity has caused naturally-occurring CO2 to continuously bubble up from the seabed. These “CO2 seeps” have created localised changes to seawater acidity similar to those expected throughout the world’s oceans by the end of this century if CO2 emissions continue unabated.
“These seeps provide important clues to what the marine world might look like in the future,” he says.
“Our analysis of samples collected more than half a kilometre from these seeps revealed healthy and diverse communities of forams, similar to those you would find on the Great Barrier Reef. However, the samples we took closer to the seeps, where CO2 concentrations were higher, showed a very different picture.
“In the high CO2 conditions closer to the seeps, the water was more acidic, and disturbingly the number and diversity of forams was significant lower. We also observed intermediate effects of acidification on forams such as corroded or ‘pitted’ shells.
“Of most concern, not one single species of foram was found in samples drawn from locations where conditions had already reached acidification levels predicted for our oceans by 2100 in all but the most optimistic emissions scenario.”
Mass Extinction Echos
The results echo mass extinctions of marine organisms that occurred millions of years ago, when the Earth experienced significant increases in CO2, temperature or both. Although some forams were able to survive during these past events, the current rate of CO2 increase is much faster than anything seen before.
“In previous studies at these seeps we looked at the response of other organisms, such as corals – we found similar if less dramatic results – many coral species were unable to grow in these increasingly acidic conditions,” says Dr. Katharina Fabricius, a co-author of the present study.
“In the grand scheme of things, the small and simple nature of forams might make them seem fairly unimportant compared to say, corals,” Dr. Fabricius continued.
“However, foram shells account for up to 40% of the composition of some cays and sandy sea beds of coral reefs – and these habitats are home to a significant number of coral reef species such as seabirds and turtles.
“Of course the long-term implications of any disappearance of forams from the reef are not certain and will require further investigation, but these findings do add to concerns regarding the health resilience of coral reefs if ocean acidification progresses as predicted under current CO2 emission scenarios.
SOURCES
From materials released by the Australian Institute of Marine Science, AIMS.
The paper “High risk of extinction of benthic foraminifera in this century due to ocean acidification” by S. Uthicke, P. Momigliano and K. E. Fabricius appears in the Nature Publishing journal Scientific Reports. (http://www.nature.com/srep/2013/130503/srep01769/full/srep01769.html).





